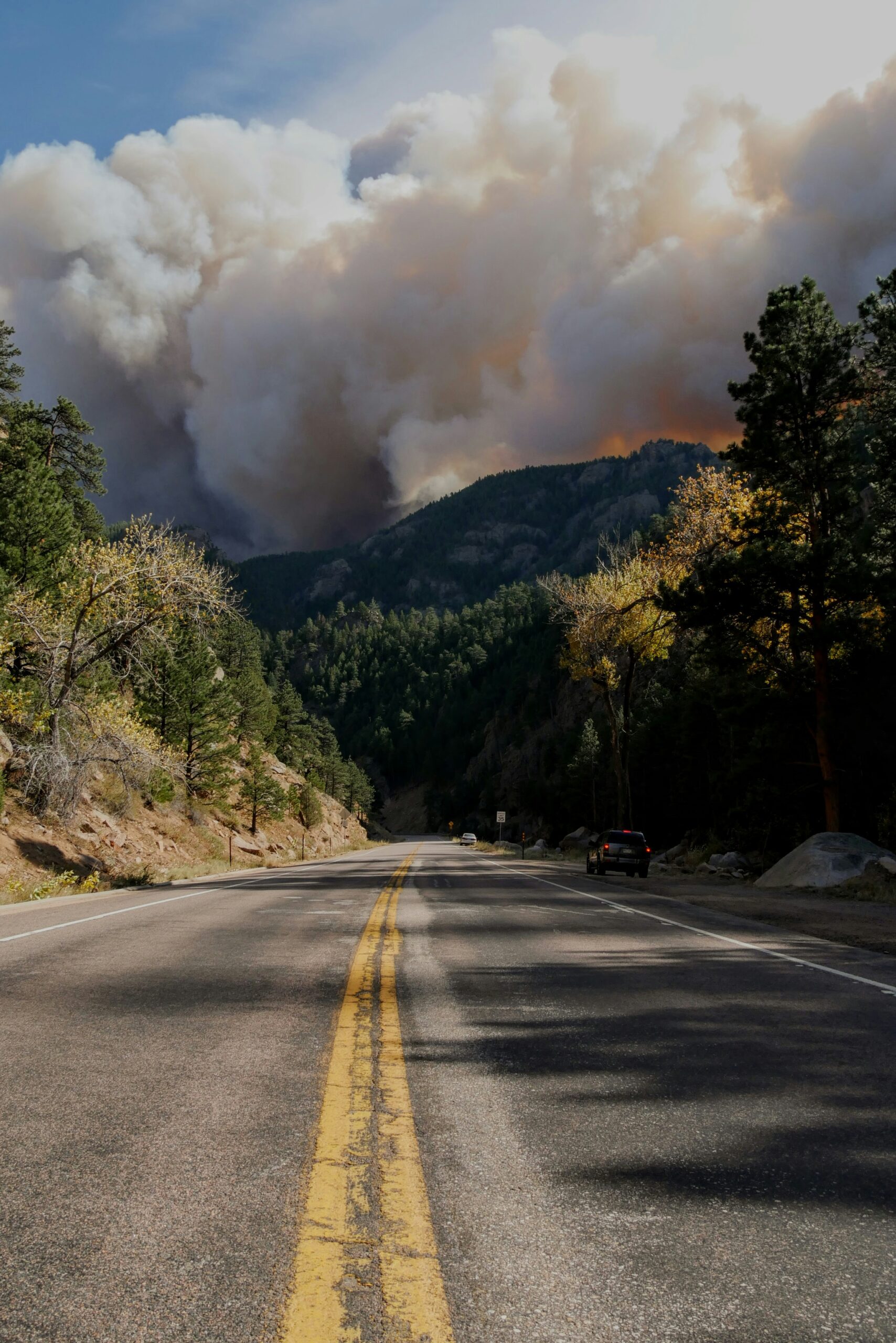
Southern Europe is currently grappling with an unprecedented wildfire crisis, marked by an escalation in both the frequency and intensity of the fires. The impact has been particularly severe in countries such as Spain, Italy, Greece, and Portugal, where vast swathes of forested areas and rural communities have been ravaged. This alarming trend can be attributed to a confluence of factors, most notably the unusual weather patterns exacerbated by climate change.
Over the past few months, the region has experienced prolonged periods of drought, coupled with record-breaking temperatures and strong winds, creating a perfect storm for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. These extraordinary climatic conditions have rendered traditional fire management strategies increasingly ineffective, putting immense pressure on firefighting resources and personnel. The rising number of incidents and their growing magnitude have also led to significant ecological destruction, economic losses, and, tragically, human casualties.
The situation in Spain, for instance, has seen several regions declare states of emergency as wildfires consume large portions of their landscapes. Simultaneously, Italy and Greece have faced similar challenges, with fires causing extensive damage to both natural reserves and human settlements. Portugal, no stranger to wildfire crises, continues to battle persistent blazes that threaten its unique biodiversity and rural communities.
Scientific consensus indicates that the frequency of such extreme weather events is likely to increase as global temperatures continue to rise. This underscores the urgent need for comprehensive climate action and innovative approaches to fire management and prevention. Understanding the dynamics of this crisis is crucial, not only for immediate response efforts but also for long-term strategies aimed at mitigating the devastating effects of wildfires in Southern Europe.
Climate Change and Its Role in Increasing Wildfire Risk
Climate change has markedly disrupted weather patterns, significantly elevating the risk of wildfires across Southern Europe. Scientific consensus affirms that global warming has escalated the frequency and intensity of wildfires due to a variety of altered environmental conditions. One prominent consequence of climate change is the prolongation of dry seasons. Extended periods without precipitation render vegetation increasingly dry and flammable, thus creating optimal conditions for wildfires to ignite and proliferate.
Higher temperatures, another upshot of global warming, further exacerbate this issue. As average temperatures rise, moisture in soil and vegetation diminishes more rapidly, thus intensifying drought conditions. According to the European Environment Agency, temperatures in Southern Europe have been rising faster than the global average. This trend directly correlates with an increased number of wildfires, both in frequency and in severity. Recent studies indicate that for every one-degree Celsius rise in temperature, the likelihood of wildfires increases by approximately 30% in Mediterranean regions.
In addition to prolonged dry spells and higher temperatures, more intense and erratic wind patterns have also been observed. These winds can rapidly spread fires over extensive areas, complicating efforts to control them. Expert opinions underline that shifting jet streams and other atmospheric changes, driven by climate change, contribute significantly to these hazardous wind conditions. For instance, the infamous Mistral winds now exhibit more intense behaviors, leading to rapid wildfire propagation across Southern Europe.
Scientific research over the past few decades has consistently drawn a direct line between global warming and increased wildfire risk. Various models and simulations support the assertion that as climate change progresses, the conditions favorable for wildfires will continue to become more prevalent. Thus, understanding and mitigating the influence of climate change on wildfire risk is pivotal for devising effective management and prevention strategies.
Wildfires, particularly in Southern Europe, inflict significant economic and environmental damages. Economically, the costs are multifaceted, impacting property, agriculture, and tourism. Damage to property is immediate and extensive, with entire communities often requiring reconstruction. The loss of homes, commercial establishments, and infrastructure necessitates substantial financial aid and insurance settlements.
Agriculture, a critical sector in Southern Europe, is severely affected. Wildfires decimate crops, orchards, and vineyards, leading to substantial financial losses for farmers and disrupting food supply chains. Consequently, regional economies suffer, amplifying the economic burden as the cost of food rises due to shortages. The tourism industry, a vital economic engine for many Southern European countries, also incurs significant losses. Iconic landscapes and cultural landmarks lose their appeal when ravaged by fires, leading to drops in tourist numbers and revenues.
Beyond immediate economic impacts, the environmental consequences of wildfires are profound and long-lasting. One significant effect is the loss of biodiversity. Southern Europe is home to a vast array of plant and animal species, many of which are lost during wildfires. The destruction of habitats further threatens endangered species, pushing some closer to extinction.
Soil degradation is another critical environmental issue resulting from wildfires. The intense heat and subsequent vegetation loss make soils more prone to erosion. Nutrients essential for plant growth get stripped away, making recovery for the affected areas slow and difficult. In turn, this degradation affects agricultural productivity and forest regrowth.
Additionally, wildfires contribute significantly to carbon emissions, exacerbating climate change. Burning vegetation releases large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which, in the long term, affects global weather patterns and further elevates the risk of future wildfires.
Several notable case studies illustrate these impacts. The 2017 wildfires in Portugal serve as a stark example, where over 100 lives were lost, and economic damages exceeded €1 billion. Similarly, in Greece, the devastating 2018 fires in Mati left a haunting legacy of both human and financial loss, highlighting the urgent need for improved wildfire management and prevention strategies.
Human Factors and Land Management
Human activities significantly escalate the risk of wildfires across Southern Europe. Arson, whether driven by malicious intent or accident, remains one of the most prominent triggers of these devastating events. However, deliberate burning is not the sole catalyst; land mismanagement also plays an instrumental role. The expansion of urban areas into previously untouched forested regions increases the potential ignition points and complicates efforts to control fires once they start. Urban sprawl, combined with inadequate zoning laws, heightens vulnerability.
Inadequate forest management is another critical factor exacerbating wildfire risks. Poorly maintained forests, with accumulated dry vegetation and insufficient firebreaks, become tinderboxes waiting for a spark. Forestry experts highlight that proactive measures, such as regular clearing of underbrush and the controlled burning of debris, can notably decrease the likelihood of large-scale fires. Despite these insights, many regions suffer from a lack of resources or political will to implement comprehensive forest management strategies.
Deforestation further compounds the problem, as the removal of trees destabilizes ecosystems and leaves large areas of land exposed and vulnerable. Additionally, the abandonment of agricultural land contributes to the problem. Once agricultural fields are left uncultivated, they quickly become overgrown with shrubs and grasses that can easily catch fire. Experts in forestry and local authorities consistently call for the reactivation of these areas through sustainable agricultural practices and the integration of agroforestry systems to reduce fire risks.
Best practices for mitigating these risks, as suggested by forestry experts and local authorities, include creating and maintaining firebreaks, engaging in controlled burns during low-risk seasons, and improving urban planning to prevent the encroachment of development into fire-prone areas. Furthermore, community education and robust monitoring systems are essential to detect and prevent potential fire hazards promptly. Addressing these human factors through informed policies and collaborative efforts will be crucial in reducing the threat of wildfires across Southern Europe.
Emergency Response and Preparedness
Southern Europe has been experiencing an increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires, prompting a rigorous examination of existing emergency response and preparedness frameworks. Various Southern European countries have established multifaceted strategies to combat wildfires, involving government policies, local fire services, and, when necessary, international aid.
Government policies play a pivotal role in shaping emergency responses. Spain, Greece, and Italy, for instance, have dedicated wildfire management plans that include controlled burns, forest management, and the allocation of resources for rapid response measures. Spanish strategies are particularly noted for integrating advanced satellite monitoring systems that provide real-time data to forecast wildfire behavior. Similarly, Greece has implemented stringent regulations to mitigate fire risks, such as prohibiting outdoor burns during peak seasons.
Local fire services are essential in the execution of these plans. Firefighters across Southern Europe are equipped with specialized training to handle varying wildfire scenarios, often working in hazardous conditions to safeguard communities. However, despite their valiant efforts, these local services frequently encounter limitations, such as insufficient staffing, outdated equipment, and underfunding.
When national efforts are overwhelmed, international aid becomes crucial. The European Union’s Civil Protection Mechanism exemplifies the collective action approach, providing resources and support to member states during wildfire emergencies. In recent years, additional support has come from countries outside the EU, amplifying response capabilities during peak periods of wildfire activity.
Nonetheless, significant gaps in preparedness persist. Early warning systems, for example, are not uniformly effective across the region. There’s an urgent need for a unified, cross-border early warning framework that leverages the latest technological advancements in predictive analytics. Furthermore, community education initiatives are often sporadic and underfunded. Greater emphasis on educating the public about fire prevention and response could mitigate the devastation caused by wildfires.
In light of these insights, enhancing emergency response and preparedness in Southern Europe is imperative. A holistic approach involving robust government policies, well-equipped local fire services, and coordinated international aid, complemented by advanced early warning systems and comprehensive community education, is vital for combating the escalating threat of wildfires.
Innovative Technologies and Techniques in Wildfire Management
The escalating wildfire threat in Southern Europe has necessitated the development and deployment of innovative technologies and techniques to predict, monitor, and control such disasters effectively. Among the forefront of these advancements is the use of satellite imagery. Satellites equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors provide real-time data, enabling authorities to monitor large forested areas, identify potential fire hotspots, and assess damage post-incident. The European Space Agency, for instance, employs the Sentinel-2 satellite to deliver critical information that aids in rapid response and decision-making.
In conjunction with satellite technology, drones have emerged as a critical tool in wildfire management. They offer the flexibility of closer inspections and are particularly effective in accessing remote or hazardous areas that are challenging for ground crews. Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras can detect heat signatures of ignitions, helping to identify fire outbreaks promptly before they spiral out of control. In Portugal, drones have successfully been used to survey forest conditions, providing invaluable data that supports firefighting strategies and the coordination of ground teams.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed wildfire prediction models, significantly enhancing their accuracy and reliability. AI-powered platforms analyze vast datasets, including weather conditions, vegetation types, historical fire data, and real-time satellite images, to anticipate wildfire behaviors and potential ignition points. The FlamMap fire mapping and analysis system in Spain leverages such AI capabilities to simulate fire spread and intensity, helping local authorities to allocate resources more efficiently and implement preventative measures.
On the ground, advanced firefighting equipment has been instrumental in combating wildfires. Tools such as fire-retardant gels, automated water cannons, and portable heavy-duty pumps that deliver enhanced water pressure enable firefighter teams to tackle blazes more effectively and safely. In Greece, the incorporation of these innovative solutions has markedly improved the capacity to control and extinguish wildfires, minimizing their devastating impacts on communities and natural habitats.
The integration of these cutting-edge technologies and techniques in Southern Europe and beyond illustrates a proactive approach to wildfire management. By leveraging satellite imagery, drones, AI-based prediction models, and advanced firefighting equipment, authorities can better anticipate, monitor, and counteract the threats posed by wildfires, ultimately fostering more resilient and prepared communities.
Community involvement plays a crucial role in wildfire prevention and management, particularly in regions prone to high to extreme wildfire risks like Southern Europe. Ensuring that residents are educated and actively participating in fire safety protocols can significantly mitigate the potential hazards posed by wildfires.
Education and Awareness Programs
Educational initiatives aimed at increasing fire safety awareness are pivotal. These programs typically focus on informing residents about the risks of wildfires, the importance of maintaining defensible space around properties, and the appropriate measures to take in the event of a wildfire. Workshops, community meetings, and school programs are common methods used to disseminate this vital information. By equipping residents with the knowledge to prevent and respond to wildfires, these programs enhance communal resilience and preparedness.
Creating Firebreaks
Community involvement extends to physical measures such as the creation of firebreaks. Firebreaks, which are gaps in vegetation that act as barriers to slow down or stop the spread of flames, can be established through collective effort. Local volunteers often collaborate with firefighting agencies to clear vegetation and create these crucial defense lines. The implementation of firebreaks not only provides immediate protection but also fosters a sense of responsibility and cohesion among community members.
Developing Evacuation Plans
Another critical aspect of community-based wildfire management is the development of evacuation plans. These plans are designed to ensure swift and safe evacuation of residents in the event of an approaching wildfire. Community-wide drills and the distribution of evacuation maps are integral components of these plans. Encouraging residents to participate in these preparedness exercises enhances their readiness and increases the likelihood of a successful and orderly evacuation.
Impact of Community-led Efforts
There are numerous stories of community-led efforts significantly reducing wildfire risks. For instance, in Spain, a small village successfully implemented a community fire safety program that involved regular vegetation clearance and public education sessions. As a result, the village experienced fewer wildfire incidents and demonstrated improved communal coordination during emergencies. Similarly, in Italy, a grassroots initiative led to the creation of an extensive network of firebreaks, which played a vital role in preventing the spread of wildfires in the region.
Overall, the active involvement of community members in wildfire prevention and management strategies is indispensable. By fostering a culture of awareness, preparedness, and collective action, communities can markedly reduce the risks and impacts of wildfires, ensuring greater safety and resilience in wildfire-prone areas.
Future Outlook and Long-term Solutions
As climate change continues to intensify, the risk of wildfires in Southern Europe is projected to escalate further. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and unpredictable weather patterns make the region increasingly susceptible to wildfires. Scientists warn that without significant intervention, the frequency and severity of these catastrophic events are likely to increase in the coming decades, posing a considerable threat to both ecosystems and human communities.
Addressing the escalating wildfire risk requires a multifaceted approach, where proactive policy changes play a critical role. Governments must invest in robust wildfire prevention strategies, including stringent land-use regulations and enhanced forest management practices. Policies that incentivize the reduction of flammable vegetation through controlled burns and promote the construction of fire-resistant infrastructure are imperative to mitigate the potential damage.
Reforestation projects offer another viable long-term solution. Replanting native species and creating green firebreaks can help restore degraded forests, improve biodiversity, and reduce the spread of fires. These efforts should be complemented by community involvement and education programs aimed at raising awareness about wildfire prevention and response techniques.
International cooperation is essential in combatting the transboundary nature of wildfires. Countries in Southern Europe must collaborate, sharing resources, technological innovations, and expertise in wildfire management. Platforms for bilateral and multilateral cooperation can strengthen disaster preparedness and enable more efficient response strategies.
A call to action is critical now more than ever. Governments, organizations, and individuals must invest in sustainable practices and preventive measures to curb the high to extreme risk of wildfire across Southern Europe. By fostering a collective commitment to environmental stewardship, we can safeguard our natural landscapes and communities from the growing threat of wildfires.