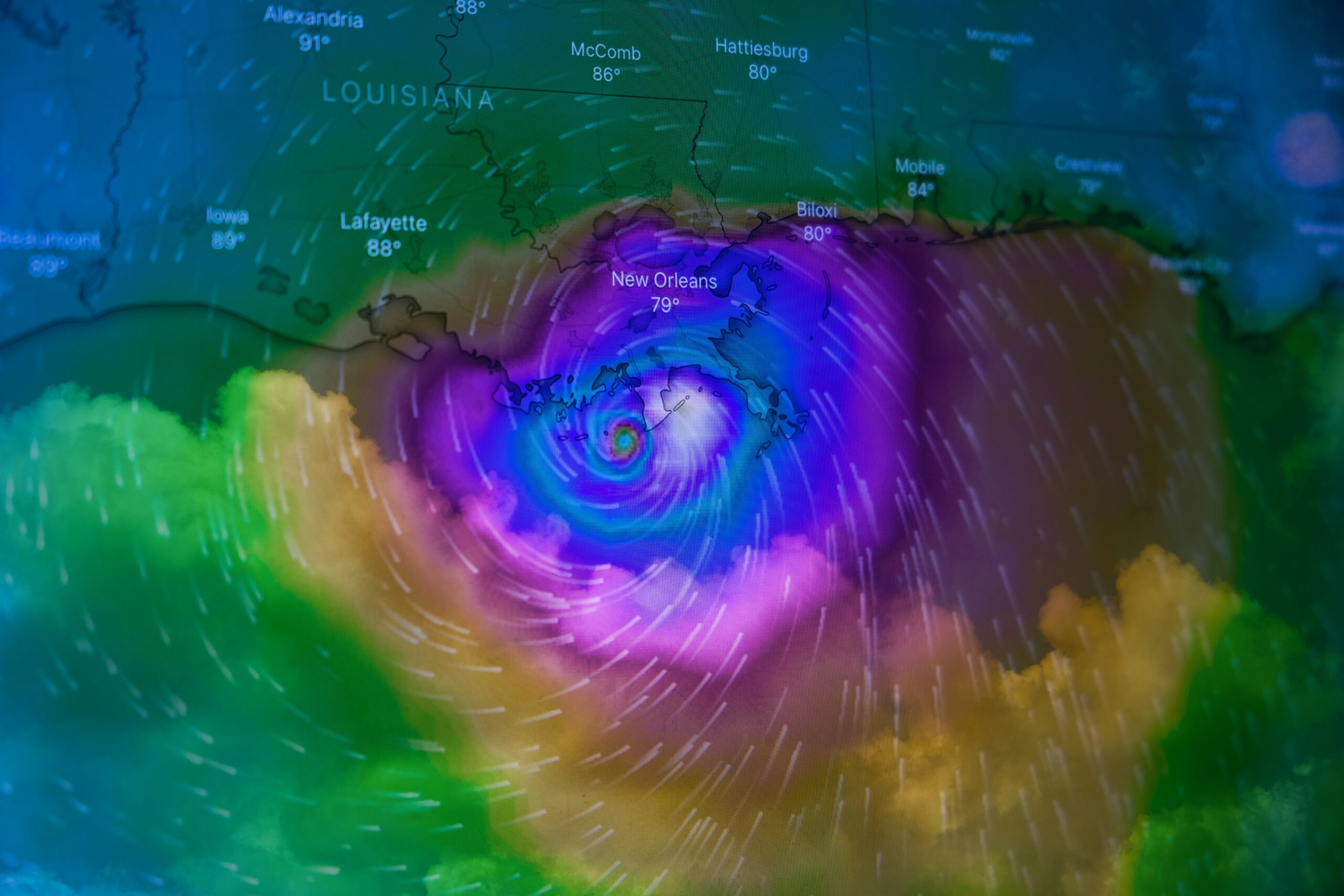
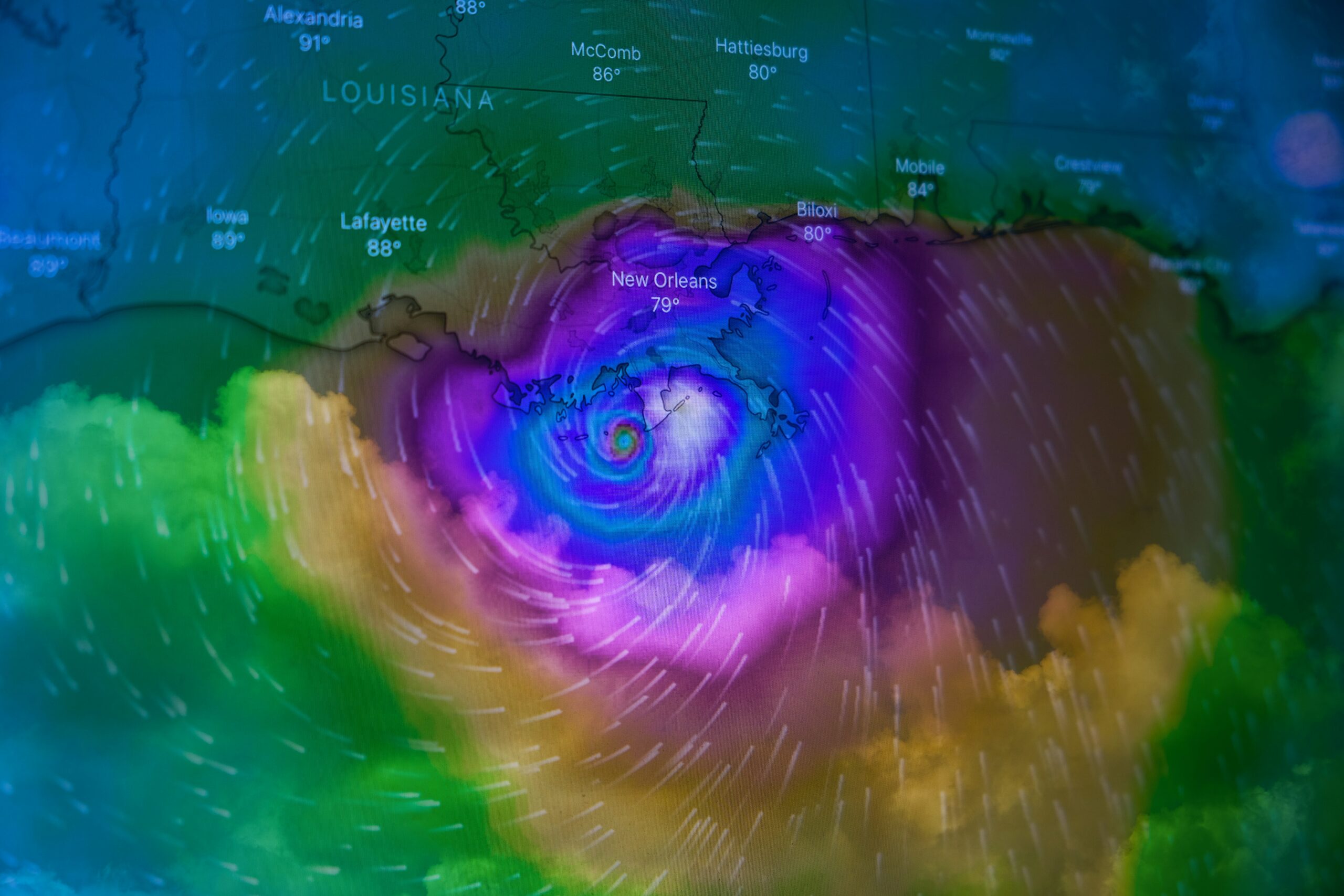
Introduction to the Severe Thunderstorm Watch
A severe thunderstorm watch has been issued for Ontario and Quebec, signalling the potential for hazardous weather conditions in these regions. A severe thunderstorm watch is an alert that indicates conditions are favorable for the development of severe thunderstorms that could produce damaging weather phenomena. This watch serves as a critical early warning, prompting residents and local authorities to stay vigilant and prepared for sudden changes in weather.
The current watch encompasses various areas across Ontario and Quebec, including both urban and rural locales. The primary concerns associated with this watch are the possibilities of nickel-sized hail and heavy downpours. Nickel-sized hailstones can cause significant damage to property, vehicles, and crops, while heavy downpours may lead to localized flooding, reduced visibility, and hazardous driving conditions.
Meteorologists monitor weather patterns constantly, looking for signs that could lead to severe thunderstorms. Factors such as atmospheric instability, moisture levels, and wind patterns are scrutinized to determine the likelihood of severe weather. When these indicators align, a watch is issued to alert the public of the potential for severe thunderstorms, allowing people the opportunity to take necessary precautions and stay safe.
Currently, the areas affected by this severe thunderstorm watch include major cities and smaller communities alike, with weather services urging everyone within the watch zone to remain aware of the evolving weather conditions. It is recommended to stay tuned to local weather updates, secure loose items outdoors, and prepare for possible power outages. By understanding the significance of a severe thunderstorm watch and the potential hazards it implies, residents of Ontario and Quebec can better protect themselves and their property from the impending severe weather.
Understanding Severe Thunderstorms
Severe thunderstorms are formidable weather phenomena characterized by their intensity and potential for significant damage. Unlike regular thunderstorms, which are often marked by lightning, thunder, and moderate rain, severe thunderstorms are distinguished by their capacity to produce extreme weather conditions such as large hail, strong winds, and torrential downpours. These elements can lead to considerable harm to property, infrastructure, and even pose risks to human safety.
The development of severe thunderstorms is intricately linked to specific meteorological conditions. One of the primary factors is atmospheric instability, which occurs when there is a significant temperature difference between the upper and lower layers of the atmosphere. This disparity causes warm, moist air near the ground to rise rapidly into the colder air above. As this warm air ascends, it cools and condenses, forming towering cumulonimbus clouds that are a hallmark of thunderstorms.
Moisture is another critical ingredient in the formation of severe thunderstorms. Adequate moisture in the lower atmosphere provides the necessary fuel for storm development. When combined with atmospheric instability, this moisture can lead to the formation of large and intense storm systems capable of producing heavy rainfall and hail. The presence of sufficient moisture also contributes to the longevity of the storm, allowing it to sustain itself over an extended period.
In addition to instability and moisture, lift is a crucial component in the genesis of severe thunderstorms. Lift can be generated through various mechanisms, such as frontal boundaries, where warm and cold air masses collide, or through topographical features like mountains. This lifting process forces the warm, moist air to rise, further enhancing the development of severe thunderstorms.
In essence, severe thunderstorms are a result of a complex interplay of atmospheric instability, moisture, and lift. These storms differ from regular thunderstorms not only in intensity but also in their potential to cause substantial damage through phenomena like nickel-sized hail, strong winds, and flash flooding. Understanding these underlying conditions is essential for predicting and preparing for severe weather events, particularly in regions such as Ontario and Quebec, which are currently under a severe thunderstorm watch.
Weather Patterns Leading to the Watch
The severe thunderstorm watch currently in effect for Ontario and Quebec is the result of a complex interplay of atmospheric conditions. Key among these is the presence of a low-pressure system that has been steadily advancing from the west. This system is characterized by a robust frontal boundary that is generating significant instability in the atmosphere. As the low-pressure system moves eastward, it is colliding with warm, moist air masses originating from the Gulf of Mexico. This convergence of contrasting air masses is a primary driver for the development of severe thunderstorms.
Moreover, upper-level wind patterns are playing a crucial role in the current weather scenario. A strong jet stream is positioned over the region, providing additional lift and shear. This combination of surface-level convergence and upper-level divergence is creating an environment conducive to the formation of severe convective activity. The jet stream’s influence is also enhancing the potential for strong updrafts within thunderstorm cells, which can lead to the production of nickel-sized hail.
Additionally, the humidity levels in Ontario and Quebec have been notably high over the past few days, contributing to the overall instability of the atmosphere. Elevated dew points are indicative of the abundant moisture available for storm development. This, coupled with daytime heating, is further destabilizing the air mass, increasing the likelihood of downpours and localized flooding.
In summary, the severe thunderstorm watch is the result of a synergistic effect of a low-pressure system, frontal boundaries, upper-level jet stream dynamics, and high humidity levels. These factors collectively create an environment ripe for severe weather, including the potential for significant hail and heavy rainfall. Residents of Ontario and Quebec are advised to stay informed and prepared as these conditions continue to evolve.
Potential Hazards: Nickel-Sized Hail
Nickel-sized hailstones are a significant concern during severe thunderstorms, particularly for regions like Ontario and Quebec. Hailstones form when updrafts in thunderstorms carry raindrops upward into extremely cold areas of the atmosphere, where they freeze. As these ice particles are repeatedly lifted by strong updrafts, they accumulate additional layers of ice, growing in size with each cycle. When the hailstones become too heavy for the updrafts to support, they fall to the ground, potentially causing considerable damage.
The impact of nickel-sized hailstones on people, property, and agriculture can be substantial. For individuals caught outdoors, hail of this size can cause injuries ranging from bruises to lacerations. It’s essential to seek shelter immediately when a hailstorm is imminent to avoid such hazards. In terms of property damage, vehicles, roofs, windows, and siding are particularly vulnerable. Hail can dent cars, shatter glass, and create costly damages to building exteriors.
Agricultural sectors in Ontario and Quebec are also at risk during hailstorms. Crops such as fruits, vegetables, and grains can suffer severe damage, leading to financial losses for farmers. Hailstones can strip leaves, break stems, and bruise produce, significantly reducing the quality and quantity of the harvest. In some cases, entire fields can be rendered unproductive for the season, impacting local food supplies and economies.
In summary, while nickel-sized hailstones might seem small, their potential to cause widespread damage should not be underestimated. Understanding how hail forms and preparing for its impacts are crucial steps for residents and businesses in the affected areas. By staying informed and taking precautionary measures, the adverse effects of such severe weather phenomena can be mitigated.
Potential Hazards: Downpours
Severe thunderstorms forecasted for Ontario and Quebec carry a significant risk of heavy downpours. These intense rain events can lead to flash flooding, which poses a substantial threat to both urban and rural areas. Urban regions, with their extensive impermeable surfaces such as roads and sidewalks, are particularly vulnerable as water cannot easily be absorbed into the ground, leading to rapid accumulation and potential flooding. Rural areas are not exempt, especially where the terrain may channel water into lower-lying regions.
The risk of flash flooding is compounded by the potential for reduced visibility during heavy downpours. Motorists may find themselves struggling to see the road ahead, increasing the likelihood of accidents. This reduced visibility affects not only drivers but also pedestrians and cyclists, making streets and highways particularly hazardous. Additionally, the downpours may disrupt public transportation, causing delays and cancellations.
Hazardous driving conditions are another critical concern. Slick roads, combined with reduced visibility, create a perilous environment for anyone traveling during these storms. Hydroplaning, where a vehicle’s tires lose traction with the road surface due to a layer of water, can lead to loss of control and serious accidents. For this reason, it’s crucial to slow down and maintain a safe distance from other vehicles to mitigate the risk of collisions.
To stay safe during heavy rain events, it is advisable to monitor weather updates regularly. Avoid traveling during peak storm periods if possible, and if you must drive, ensure your vehicle is in good condition, especially the tires and brakes. Keep headlights on to improve visibility for yourself and others. If you find yourself caught in a downpour, pull over to a safe location until the worst of the storm passes. Additionally, never attempt to cross flooded areas on foot or in a vehicle, as the water’s depth and force can be deceptively hazardous.
Emergency Preparedness and Safety Tips
Severe thunderstorms can pose significant risks, making it crucial for residents of Ontario and Quebec to take appropriate measures to ensure their safety and preparedness. One of the primary steps in preparing for a severe thunderstorm is to assemble a comprehensive emergency kit. This kit should include essential items such as non-perishable food, water, flashlights, batteries, a first aid kit, and any necessary medications. Additionally, it’s advisable to have important documents and emergency contact information readily accessible.
Securing outdoor objects is another vital precaution. Loose items like patio furniture, umbrellas, and gardening tools can become dangerous projectiles during high winds. Ensuring these items are either brought indoors or properly secured can mitigate potential damage and injuries. Homeowners should also inspect their properties for weak tree branches that could fall and cause harm or damage during the storm.
For those caught outside during a severe thunderstorm, immediate action is essential. Seeking shelter in a sturdy building is the safest option. If shelter is not available, avoid open fields, hilltops, and isolated trees, as these areas are more susceptible to lightning strikes. It’s also advisable to stay away from water bodies and metal objects that can conduct electricity.
Staying informed through reliable weather alerts is critical. Weather apps, local news stations, and government websites provide timely updates on storm conditions and warnings. Residents are encouraged to heed these alerts and be prepared to take immediate action if necessary. Having a battery-operated weather radio can also be beneficial in case of power outages, ensuring continuous access to crucial information.
By taking these proactive steps, individuals can enhance their preparedness for severe thunderstorms and reduce the risks associated with such extreme weather events. Awareness and preparedness are key components in safeguarding oneself and one’s property during severe weather conditions.
Impact on Communities and Infrastructure
Severe thunderstorms in Ontario and Quebec can have significant repercussions on both communities and infrastructure. One of the immediate concerns during such weather events is the likelihood of power outages. High winds and hail can damage power lines and transformers, leading to widespread electrical disruptions. These outages can last from a few hours to several days, depending on the severity of the storm and the efficiency of the response teams. Residents and businesses must therefore be prepared for these eventualities by having backup power sources and emergency kits ready.
Buildings and other structures are also highly vulnerable during severe thunderstorms. Nickel-sized hail can cause considerable damage to roofs, windows, and vehicles. Prolonged downpours might lead to flooding, especially in areas with inadequate drainage systems. This flooding can compromise the structural integrity of buildings and homes, increasing the risk of long-term damage and costly repairs. Communities need to ensure that buildings are well-maintained and that there are sufficient flood defenses in place to mitigate these risks.
Transportation networks are another critical area impacted by severe weather. Thunderstorms can lead to hazardous driving conditions, including reduced visibility, slippery roads, and the potential for accidents. Public transportation services such as buses and trains may also experience delays or cancellations. Airports could face flight disruptions, causing a ripple effect on travel plans. Ensuring that transportation systems are resilient and that there are effective communication channels in place can help manage these disruptions and ensure the safety of all commuters.
The role of local authorities and emergency services is paramount in such scenarios. They are responsible for issuing timely weather alerts and warnings, coordinating evacuation procedures if necessary, and providing assistance to affected residents. Collaboration between municipal services, utility companies, and emergency responders ensures a more coordinated and efficient response. Public awareness campaigns and preparedness drills can further enhance community resilience against severe thunderstorms, reducing the potential for damage and loss of life.
Conclusion and Looking Ahead
In conclusion, the potential for severe thunderstorms in Ontario and Quebec underscores the importance of being vigilant and prepared. With the possibility of nickel-sized hail and heavy downpours, residents should take proactive measures to protect themselves and their property. Staying informed through reliable weather alerts and forecasts is crucial during this period of heightened weather activity.
The recent weather patterns suggest that this region could continue to experience volatile weather conditions. Long-term forecasts indicate a prevalence of severe weather events as atmospheric conditions evolve. It is advisable to regularly check updates from meteorological services and local authorities to remain aware of any changes in weather patterns that may impact the area.
To stay updated, individuals can utilize various resources, including weather apps, local news channels, and official government websites. These platforms provide real-time information and actionable advice, ensuring that the community is well-prepared for any eventualities. Additionally, understanding the significance of alerts such as a severe thunderstorm watch can help in making informed decisions and taking timely action.
As we look ahead, it is clear that climate variability will continue to influence weather patterns in Ontario and Quebec. Being prepared for severe thunderstorms and other extreme weather events is essential for safety and resilience. By staying informed and taking appropriate precautions, residents can mitigate the risks associated with these natural occurrences. Continuous monitoring and adherence to safety guidelines will ensure that the community remains resilient in the face of adverse weather conditions.